- 详细介绍
大小鼠气溶胶气管内给药套装,可输送定量的气溶胶到大鼠、小鼠气管内和肺内,为定量化给药提供了更好的方案:直接对大鼠、小鼠、比格犬、猴子的肺部(气管内)进行定量气溶胶雾化给药,给药快捷、操作方便。
有三种型号可供选择:大鼠型气管内定量给药套装,小鼠型气管内定量给药套装,大单位气管内定量给药套装
气管内定量给药装置的主要特色:· 定量 QUANTIFIABLE:将定量的气溶胶给到动物肺部
· 定时 TIMED:可以在一个或多个时间点进行给药
· 有效 EFFECTIVE:气溶胶的吸收效果好,给药快速,效率高,操作方便
· 方便 CONVENIENCE:维护简单,操作方便

型号:YAN30012 液体气溶胶肺部给药

型号:YAN30010 干粉气溶胶肺部给药
大小鼠气管内定量给药装置的主要特点:
· 快速、精确的直接肺部给药——气溶胶无浪费;
· 纯机械动力,无外部空气进入;
· 不需加热、推进剂、超声波或压缩空气等,对药物物影响;
· 手持式设计,使用非常方便;
· 喷射头顶端圆滑的设计,保证安全、温和的插入气管内;
· 可高温高压消毒灭菌,可重复使用;
· 比其它雾化器和吸入设备提供更高浓度发药物体积或剂量;
· 比传统滴注法给药提供更均匀的药物分布;
使用方法图例:
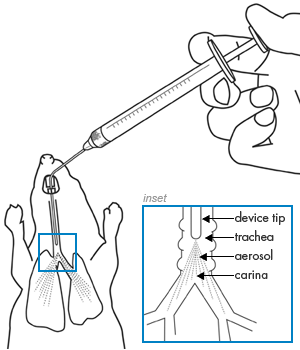
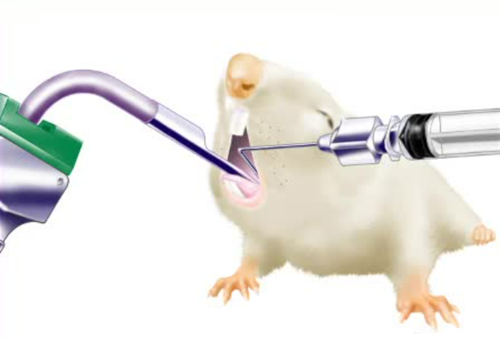
另外,可选配大小鼠气管插管喉镜、大小鼠气管插管工具包套装、大小鼠气管插管等工具,能更便捷的完成手术。
大鼠、小鼠喉镜

大小鼠气管插管工具包套装

气管插管平台(多种款式和型号可选)

CG-02M型,适合做小鼠,外尺寸:20*15*20cm
CG-02R型,适合做大鼠,外尺寸:22*21*28cm
适用于大、小鼠的气管插管手术操作

CG-04M型,小鼠型
配合铁架台使用,多角度可调;
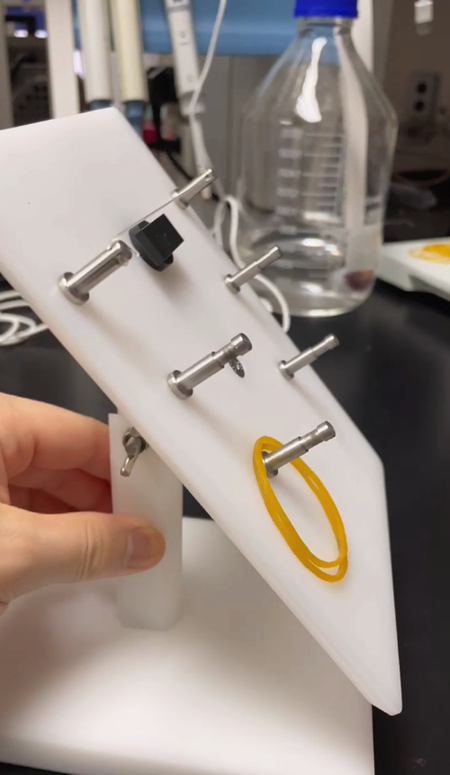

型号:CG-06M
多角度可调;
大小鼠通用,尺寸约:20*15*15cm
参考文献:
1. Li, Cheng et al. “Broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by an inhalable bispecific single-domain antibody.” Cell vol. 185,8 (2022): 1389-1401.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.009
2. Peng, Boya et al. “Robust delivery of RIG-I agonists using extracellular vesicles for anti-cancer immunotherapy.” Journal of extracellular vesicles vol. 11,4 (2022): e12187. doi:10.1002/jev2.12187
3. Wu, Lan et al. “Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles Mediate Sustained Gene Silencing and Improved Biocompatibility of siRNA Delivery Systems in Mouse Lungs after Pulmonary Administration.” ACS applied materials & interfaces vol. 13,3 (2021): 3722-3737. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c21259
4. Tian, Xidong et al. “Pulmonary Delivery of Reactive Oxygen Species/Glutathione-Responsive Paclitaxel Dimeric Nanoparticles Improved Therapeutic Indices against Metastatic Lung Cancer.” ACS applied materials & interfaces vol. 13,48 (2021): 56858-56872. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c16351
5. Gu, Peiyu et al. “Protective function of interleukin-22 in pulmonary fibrosis.” Clinical and translational medicine vol. 11,8 (2021): e509. doi:10.1002/ctm2.509
6. Su, Ruonan et al. “Venetoclax nanomedicine alleviates acute lung injury via increasing neutrophil apoptosis.” Biomaterials science vol. 9,13 (2021): 4746-4754. doi:10.1039/d1bm00481f
7. Yang, Huilin et al. “Triptolide dose-dependently improves LPS-induced alveolar hypercoagulation and fibrinolysis inhibition through NF-κB inactivation in ARDS mice.” Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie vol. 139 (2021): 111569. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111569
8. Wu, Yanqi et al. “SN50 attenuates alveolar hypercoagulation and fibrinolysis inhibition in acute respiratory distress syndrome mice through inhibiting NF-κB p65 translocation.” Respiratory research vol. 21,1 130. 27 May. 2020, doi:10.1186/s12931-020-01372-6
9. Han, Meishan et al. “Engineering of Stimulus-Responsive Pirfenidone Liposomes for Pulmonary Delivery During Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 13 882678. 25 Apr. 2022, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.882678
10. Wu, Lan et al. “Quantitative comparison of three widely-used pulmonary administration methods in vivo with radiolabeled inhalable nanoparticles.” European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V vol. 152 (2020): 108-115. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.05.004
11. Peng, Jianqing et al. “Carboxymethyl Chitosan Modified Oxymatrine Liposomes for the Alleviation of Emphysema in Mice via Pulmonary Administration.” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 27,11 3610. 4 Jun. 2022, doi:10.3390/molecules27113610







 VIP会员
VIP会员

 粤公网安备44196802000105号
粤公网安备44196802000105号